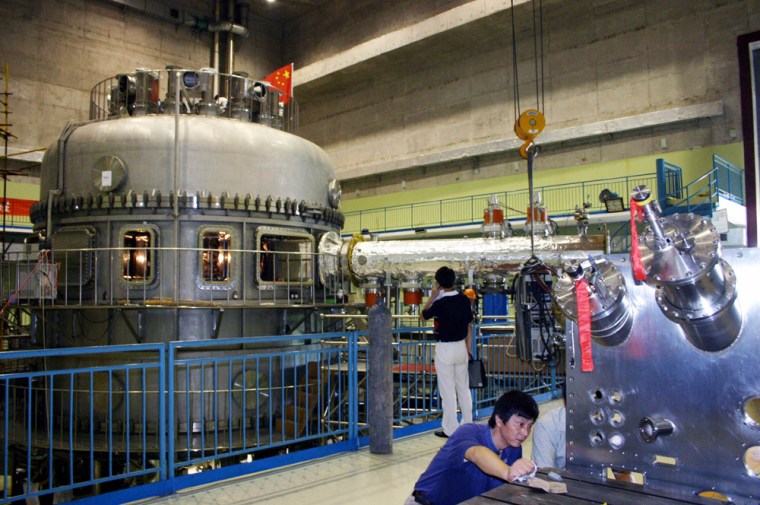
Scientists on Thursday carried out China's first successful test of an experimental fusion reactor, powered by the process that fuels the sun, a research institute spokeswoman said.
China, the United States and other governments are pursuing fusion research in hopes that it could become a clean, potentially limitless energy source. Fusion produces little radioactive waste, unlike fission, which powers conventional nuclear reactors.
Beijing is eager for advances, both for national prestige and to reduce its soaring consumption of imported oil and dirty coal.
The test by the government's Institute of Plasma Physics was carried out on a Tokamak fusion device in the eastern city of Hefei, said Cheng Yan, a spokeswoman at the institute.
Cheng said the test was considered a success because the reactor produced plasma, a hot cloud of supercharged particles. She wouldn't give other details.
"This represents a step for humankind in the study of nuclear reaction," she said.
U.S. and other scientists have been experimenting with fusion for decades but it has yet to be developed into a viable energy alternative.
"I think it is a considerable step ahead for China," said Karl Heinz Finken, a senior scientist at the Institute for Plasma Physics in Juelich, Germany, who had no role in the Chinese research.
"China is speeding up with the development of nuclear fusion and I think at the moment they are making considerable progress," he said.
The Chinese facility is similar to the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, or ITER, being built by a seven-nation consortium in Cadarache in southern France, according to state media. That reactor is due to be completed in 2015.
China is a partner in the ITER reactor, along with the European Union, the United States, Japan, Russia, India and South Korea.
A Tokamak reactor uses a doughnut-shaped magnetic field to contain the hot gas.
Several countries have produced plasma using a Tokamak or similar device, said Gabriel Marbach, deputy head of fusion research at the ITER facility. He said producing plasma was only one step toward the fusion that ITER aims to perform, and that the project could be helped by the Chinese experiments.
"It was important for China to show that it is part of the club, and that adds value to its participation in ITER," Marbach said.
"That is not to say that it is at the level of the Europeans or Americans," he said. However, he added, "We are rather admiring of the Chinese for conducting this test. It was conducted well, and they constructed (the machine) rather quickly."
China is the world's No. 2 oil consumer and its No. 3 importer, consuming at least 3.5 million barrels of foreign oil per day last year.
China plans to build dozens of nuclear power plants and is trying to promote use of cleaner alternative energy sources such as natural gas, wind power and methanol made from corn.