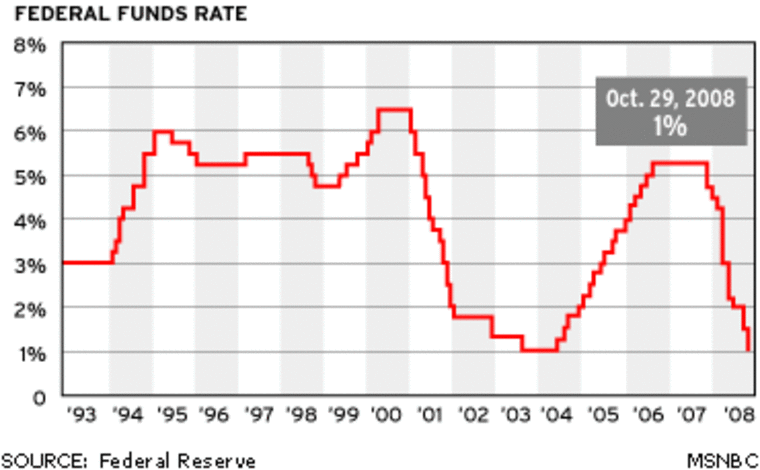
The Federal Reserve has slashed a key interest rate by half a percentage point as it seeks to revive an economy hit by a long list of maladies stemming from the most severe financial crisis in decades.
The central bank on Wednesday reduced its target for the federal funds rate, the interest banks charge on overnight loans, to 1 percent, a low last seen in 2003-2004. The funds rate has not been lower since 1958, when Dwight Eisenhower was president.
The cut marked the second half-point reduction in the funds rate this month. The Fed slashed the rate by that amount in a coordinated move with foreign central banks on Oct. 8.
In a brief statement explaining Wednesday’s action, the Fed said that the “intensification of financial market turmoil is likely to exert additional restraint on spending, partly by further reducing the ability of households and business to obtain credit.”
The central bank said that “downside risks to growth remain” holding out the promise of further rate cuts if needed. The rate-cut decision was unanimous.
Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke and his colleagues pledged that they would “monitor economic and financial developments carefully and will act as needed to promote sustainable economic growth and price stability.”
Wall Street had staged its second biggest point surge ever on Tuesday with the Dow Jones industrial average climbing by 889 points in anticipation of the Fed’s action. Trading was more subdued on Wednesday with the Dow actually slipping into negative territory immediately after the announcement, but surged up by about 200 points in late-afternoon trading.
Many analysts said they believe the Fed will not stop at 1 percent if officials see the need to cut rates further. Some are forecasting another half-point move at the Fed’s last meeting of the year on Dec. 16.
But other economists said with rates already so low, the Fed may decide to hold at 1 percent, leaving some room for a further reduction if needed next year should the country’s economic troubles intensify.
David Jones, chief economist at DMJ Advisors, said the Fed’s rate cut will be followed over the next week by similar action in other major countries as they grow more concerned that the recession that began in the United States is spreading to their regions.
But he said a section of the Fed’s statement where it listed all the efforts taken so far to battle the slowdown was a signal the central bank believes it has done enough for now.
Other economists disagreed, saying the Fed clearly lowered its worries about inflation while raising concerns about economic growth.
Sung Won Sohn, an economist at the Smith School of Business at California State University, said he believed the Fed will make the “momentous decision” to move the funds rate to zero if events in coming months show such an action is needed to battle the global credit crisis.
In its statement, the Fed indicated it had room to lower rates because the spreading economic weakness was lowering the risks that inflation would get out of control. Indeed, the weakness has caused dramatic declines in the price of oil and other commodities.
While many economists believe the country has already fallen into a recession, they think the aggressive efforts by the Fed to cut rates and take other actions to unfreeze credit markets will keep the country from plunging into a prolonged and deep downturn.
The Fed’s action was expected to be quickly followed by a reduction by commercial banks in their prime lending rate, the benchmark for millions of consumer and business loans, by a similar half-point.
The central bank also announced that it was lowering its discount rate, the interest it charges to make direct loans to banks, by a half-point to 1.25 percent. This rate has become increasingly important as the central bank has dramatically increased direct loans to banks in an effort to break the grip of the credit crisis.
Bernanke pledged in a speech earlier this month that the Fed “will not stand down until we have achieved our goals of repairing and reforming our financial system and restoring prosperity.”
In addition to the rate cuts, the Fed has been moving to pump billions of dollars into the banking system to help unfreeze markets that seized up in dramatic fashion last month. The ensuing meltdown of financial markets caused the Bush administration to successfully lobby Congress to pass on Oct. 3 a $700 billion rescue package to make direct purchases of bank stock and buy up bad assets as a way of getting financial institutions to start lending again.
That money started flowing earlier this week with $125 billion going to nine of the nation’s biggest banks. Other industries, including automakers and insurance companies, are in talks with the administration to get a share of the bailout funds.
And there is pressure from lawmakers to deploy some of the bailout resources to provide mortgage guarantees to encourage more banks to rework home loans to stem a record tide of foreclosures.
Full text of Fed statement
The Federal Open Market Committee decided today to lower its target for the federal funds rate 50 basis points to 1 percent.
The pace of economic activity appears to have slowed markedly, owing importantly to a decline in consumer expenditures. Business equipment spending and industrial production have weakened in recent months, and slowing economic activity in many foreign economies is damping the prospects for U.S. exports. Moreover, the intensification of financial market turmoil is likely to exert additional restraint on spending, partly by further reducing the ability of households and businesses to obtain credit.
In light of the declines in the prices of energy and other commodities and the weaker prospects for economic activity, the Committee expects inflation to moderate in coming quarters to levels consistent with price stability.
Recent policy actions, including today’s rate reduction, coordinated interest rate cuts by central banks, extraordinary liquidity measures, and official steps to strengthen financial systems, should help over time to improve credit conditions and promote a return to moderate economic growth. Nevertheless, downside risks to growth remain. The Committee will monitor economic and financial developments carefully and will act as needed to promote sustainable economic growth and price stability.
Voting for the FOMC monetary policy action were: Ben S. Bernanke, Chairman; Timothy F. Geithner, Vice Chairman; Elizabeth A. Duke; Richard W. Fisher; Donald L. Kohn; Randall S. Kroszner; Sandra Pianalto; Charles I. Plosser; Gary H. Stern; and Kevin M. Warsh.
In a related action, the Board of Governors unanimously approved a 50-basis-point decrease in the discount rate to 1-1/4 percent. In taking this action, the Board approved the requests submitted by the Boards of Directors of the Federal Reserve Banks of Boston, New York, Cleveland, and San Francisco.