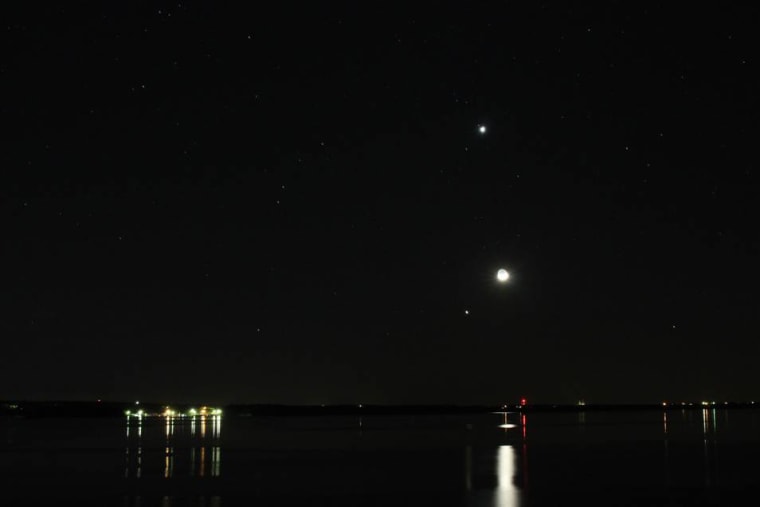
The bright planets Venus and Jupiter will perform one last sky show with the crescent moon Monday night to wrap up a two-day celestial meet-up.
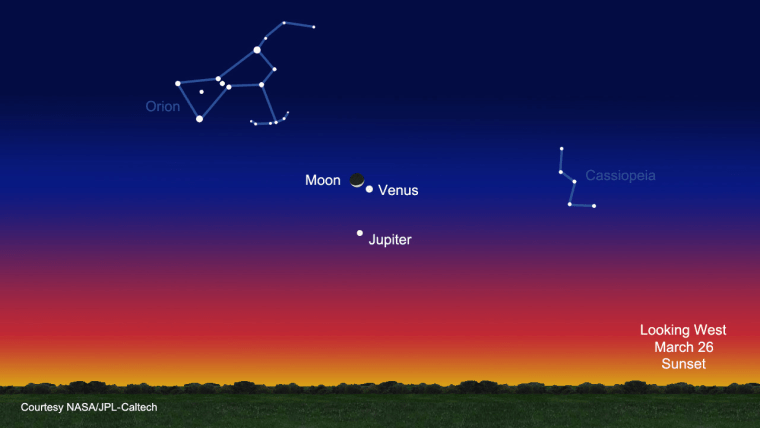
At sunset, Venus, Jupiter and the moon will appear together in the western sky in what astronomers call a conjunction. For observers with clear skies, the crescent moon will appear at the top of the trio like a giant smile in space, with Venus shining bright to the lower right and Jupiter perched below.
"This will be the best Venus-Jupiter conjunction for years to come," NASA officials wrote in a skywatching alert. "While bright to the unaided eye, they're even better when seen through a telescope – and you can share NASA's view."
On Sunday night (March 25), which marked the first night of the conjunction, NASA hosted a webchat and live telescope views of Venus, Jupiter and the moon. The space agency has archived the video via the Marshall Space Flight Center's Ustream account so latecomers can relive the experience.
"What an amazing show the universe give us!!!" skywatcher Sandy Caldarazzo of Dundalk, Md., told Space.com in an email. "I have been watching these two planets hanging out all month."
The sky map of Venus, Jupiter and the moon associated with this guide shows where to look tonight in the western sky to see the celestial sight at sunset.
While the moon, Venus and Jupiter appear close to each other in the night sky, they are actually extremely far apart.
For example, the moon is about 238,000 miles (382,900 kilometers) from Earth and appears to move quickly across the night sky. Venus and Jupiter, however, are more distant and appear to move more slowly over time. [ Amazing Photos: Venus and Jupiter in March ]
Currently, Venus is about 67 million miles (108 million km) from Earth and Jupiter is about 535 million miles (861 million km) away. Jupiter, in particular, has had a months-long run as a fantastic skywatching target, but that will soon change.
Over the next few weeks, Jupiter's appearance will slowly be lost in the glare of the setting sun.
By mid-April, the gas giant will be setting at the end of evening twilight (about 1.5 hours after sunset), then becoming harder to see as it sinks lower into the sunset. After April 24, Jupiter will disappear from the night sky until late June, when it will return in the dawn sky.
The planet Venus, meanwhile, will continue to grow brighter in the weeks ahead.
Currently, Venus is shining at its highest point above the horizon for 2012. It is visible long into the night and sets about four hours after sunset. On Tuesday, Venus will reach its easternmost point in the sky (relative to the sun) and will begin to dip back down toward the horizon.

If you have a telescope, Venus takes on a more surprising look: It appears as a bright silver-white "half moon" currently and will slowly transform into a thick crescent as its orbit brings it closer to Earth. This is because Venus, like the moon, has phases as it orbits the sun.
Venus and Jupiter are not the only planets offering dazzling views this week. The planet Mars is also visible in the eastern sky as a bright reddish-orange orb in the evening sky.
If you snap an amazing photo of Venus and Jupiter, or any other skywatching target, and would like to share it for a possible story or image gallery, please contact Space.com Managing Editor Tariq Malik at tmalik@space.com.
You can follow Space.com Managing Editor Tariq Malik on Twitter . Follow Space.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter and on .
