A new report released Thursday by the Pew Research Center says that black and Hispanic mothers, ages 40 to 44, are especially likely to have larger families.
Pew's study, which focuses on the increasing number of educated women opting for motherhood, said the decline in share of moms with four or more kids has dropped significantly among black mothers. 18% of black moms have four or more children, compared to 20% percent of Hispanic moms. In comparison, 11% of white mothers have four or more children, as do 10% of Asian moms.
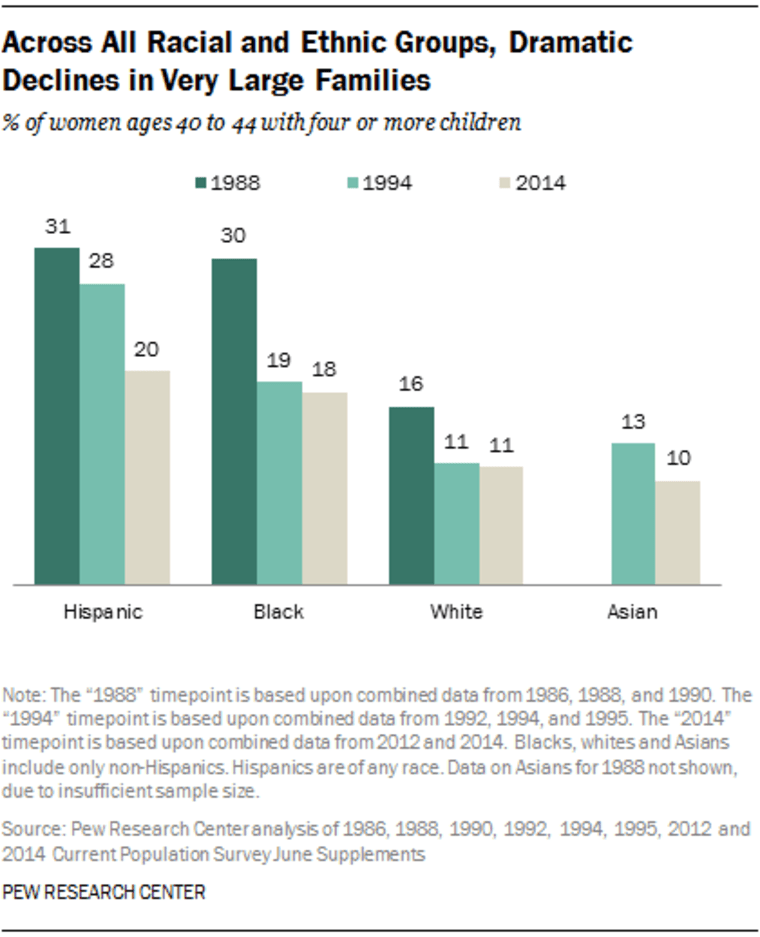
In 1988, three-in-ten black mothers ages 40 to 44 had four or more children, but by 2014, just 18% did. At the same time, the share of black mothers with one child rose by five percentage points (from 20% to 25%), as did the share with two children.
Among whites, blacks and Asians, having two children is the most common outcome for mothers. Asian moms are the most likely to have two children—fully half do. Some 44% of white moms ages 40 to 44 have two children, as do about one-third of black moms.
On average, a Hispanic mother ages 40 to 44 has had about 2.6 children. By comparison, black mothers have had about 2.5. White and Asian mothers have families that are a bit smaller, on average. White mothers have 2.3 children, and Asian mothers have 2.2 children.
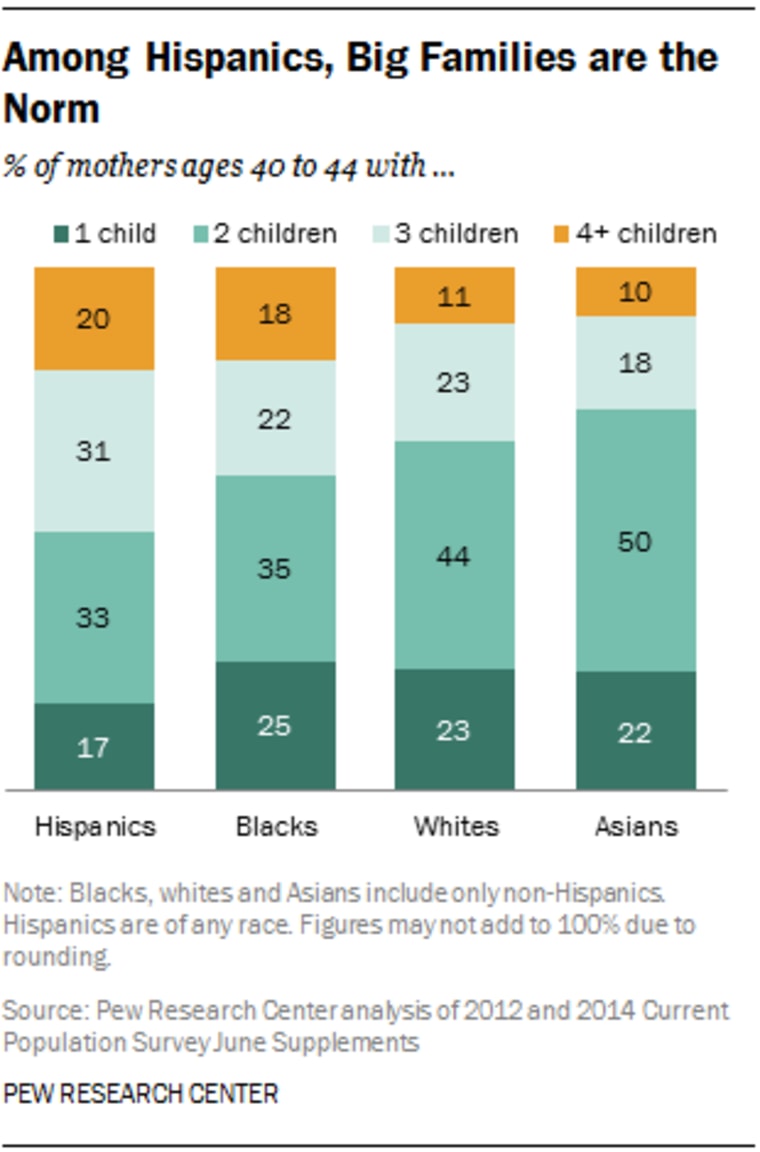
Among mothers ages 40 to 44, Hispanics are the least likely to have only one child at 17%. 25% of black moms have had just one child, as is the case for 23% of white moms and 22% of Asian moms.
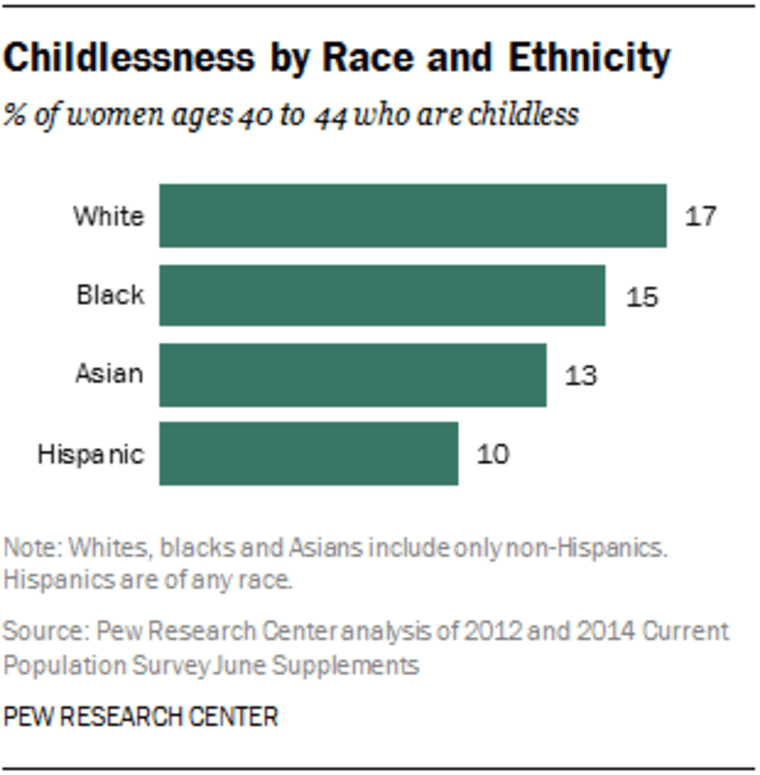
In terms of being childless, the report finds that Hispanic women are least likely to remain childless through their child-bearing years than non-Hispanic whites or blacks. Some 17% of white women ages 40 to 44 are childless, as compared with 15% of black women in the same age group, 13% of Asian women, and just 10% of Hispanic women.
Pew finds that today, 22 percent of women ages 40-44 with at least a master's degree remain childless, down from 30 percent in 1994. And on average, 60 percent of women with at least a master's degree have two or more children, up from 51 percent in 1994.

