Ever since Perriviia “Black Butterfly” Brown moved into her Memphis, Tennessee, apartment in 2015, she has been afraid to sit on her front porch. A Black transgender woman who is partially blind, Brown said she doesn’t feel safe in her neighborhood. She said she often deals with transphobic abuse when she ventures to the nearby grocery store.
“I just stay in the house and mind my business,” Brown, 46, told NBC News. “If I have someone come over, they just have to come over on the inside. I would love to entertain on the outside, but it’s … so violent out here, and you don’t know who likes you and who don’t like you, and you don’t know if they got a hatred against trans women.”
Despite her fear, Brown considers herself lucky to have a home. A 2018 Human Rights Campaign report noted that 41 percent of Black transgender respondents reported experiencing homelessness at some point in their lives, a rate five time higher than the general U.S. population.
“If you are experiencing the intersection of racism and transphobia that leads to social and economic marginalization without access to some kind of permanent housing support, it's going to be very difficult to fight to try and access that stability that a lot of people in our country take for granted.”
Dylan Waguespack
But thanks to a recent campaign that has raised over $250,000 to build a small neighborhood of 20 “tiny homes” for Black trans women and nonbinary people in the Memphis area, Brown may soon own her own home — one with a porch where she can sit outside unafraid.
“Tiny homes” are a rising trend made popular with reality TV shows like HGTV’s “Tiny House Hunters.” Seen by some as a path to affordable, minimalist living, tiny homes are pre-made studio structures, sometimes converted from sheds, that cost a fraction of the price of a traditional home.
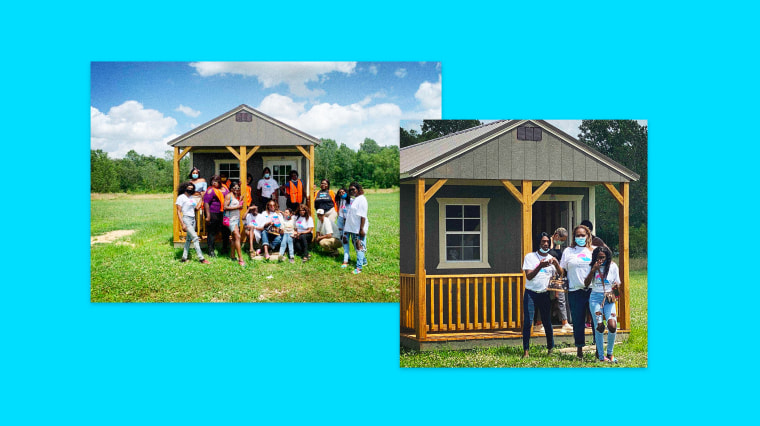
The project is the brainchild of Memphis-based My Sistah’s House, which helps Black transgender women and nonbinary people access safe housing. The small nonprofit also helps individuals with bail assistance and the legal processes around transitioning.
In June, the group launched a GoFundMe page and quickly exceeded its $200,000 goal in a matter of weeks, according to My Sistah’s House cofounder Kayla Gore.
Since its founding in 2017, My Sistah’s House has provided temporary shelter to those in the Memphis area but has struggled to help them access permanent housing, Gore said. Many of the organization’s clients have been turned away from homeless shelters due to their transgender identity, she said, adding that long-term housing projects are necessary to lift the Black trans community out of an endless cycle of homelessness and poverty.
“It's been super overwhelming to see the support that's coming in so fast and so rapidly,” Gore said. She hopes the project will serve as a model for other advocacy organizations that want to help trans people own their own homes.
Transgender homeownership
Homeownership is low among transgender people: The 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey, which included interviews with nearly 28,000 trans individuals across the U.S., found 16 percent of transgender respondents reported owning their homes, compared to 63 percent of the general public at the time.
My Sistah’s House is among a handful of trans-led, grassroots groups that are working to create long-term housing solutions for Black trans women and nonbinary people in the South.
In Atlanta, a campaign called the Homeless Black Trans Women Fund, organized by trans activist Jesse Pratt López, has so far raised over $2.7 million of its $3 million goal to create secure, long-term housing for Black transgender women. In Louisiana, Trans United Leading Intersectional Progress, or TULIP, is more than halfway to its goal of raising $400,000 to purchase and restore a six-bedroom house (to be named “House of Tulip”) that will provide a pathway to home ownership for trans and gender-nonconforming people in New Orleans.
“Housing really is this first thing that is such a necessity for people to be able to access all of these other things,” according to Dylan Waguespack, co-founder of TULIP and public policy director for True Colors United. “If you are experiencing the intersection of racism and transphobia that leads to social and economic marginalization without access to some kind of permanent housing support, it's going to be very difficult to fight to try and access that stability that a lot of people in our country take for granted.”
‘There’s so many roadblocks’
The low rate of homeownership and high rate of homelessness for transgender Americans are connected to the disproportionate discrimination, unemployment and incarceration they face, which can all cascade into a cycle of poverty, according to advocates.
Rebeckah Hill, a Memphis-based rapper, is familiar with this cycle of poverty. A Black trans woman who has experienced homelessness on and off since her early 20s, she has been unable to get her name and gender updated on her government ID, find a stable job and secure housing, or even build the credit necessary to qualify for her own home.
“I can’t get into an apartment now,” she said. “I’m 31 years old. I've never had my own place to stay.”
Black trans people have an unemployment rate more than three times that of the general population, and half of these individuals reported “feeling forced to participate in underground economy for survival,” according to a 2018 American Psychological Association report. When people turn to the “underground economy,” which includes sex work and drug sales, they then risk going to jail or prison, and a criminal record is often another barrier to obtaining long-term housing. According to the U.S. Transgender Survey, the rate of Black trans women who were incarcerated in the course of a year was 10 times the rate of the general public.
In May, Hill was incarcerated on a pending drug case. After a week in jail, she was bailed out by the Official Black Lives Matter Memphis Chapter and My Sistah’s House, which also helped her find a room in a temporary rental. Having a felony on her record, she said, has made it difficult for her to qualify for public housing and climb out of the cycle of poverty.
“There’s so many roadblocks,” Hill said. “It makes my head hurt.”
A landmark Supreme Court ruling issued last month found that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibits workplace discrimination based on sexual orientation and transgender identity. While the decision was welcome news to LGBTQ advocates, Gore noted that many Black trans women still lack access to quality education and job training that will help them begin a decent-paying career that would in turn allow them to qualify for an apartment or mortgage.
“A big portion of the folks that we serve participate in survival sex or sex work, therefore, they don't have verifiable income,” Gore said. “So that's the reason that they can't get housing or they're underemployed, in a sense that they don't necessarily have access to equitable jobs that will provide them an income that is enough to obtain stable housing.”
Currently, federal law does not explicitly prohibit discrimination based on gender identity in private housing, and at least 25 states do not have state-level protections against such discrimination, according to Movement Advancement Project, an LGBTQ think tank. While an Obama-era rule protects transgender people from discrimination in federally funded housing, the Trump administration announced it intends to reverse this measure, which could result in trans women being assigned to men’s homeless shelters.
Trans women who cannot access stable housing often seek shelter in hotel rooms, according to Hill, who said hotel managers often turn them away “because we're automatically assumed to be sex workers.”
Even when trans people meet the requirements to qualify for an apartment, they frequently report dealing with discrimination from housing providers, advocates say. According to the 2015 National Transgender Discrimination Survey, 19 percent of respondents reported being refused a home or apartment, and 11 percent reported being evicted due to their gender identity or gender expression. A 2017 Urban Institute study that relied on paired testing found that housing providers were less likely to tell transgender people about rentals. The study found that rental seekers in the Washington, D.C., metro area who told housing providers they were trans were less likely, on average, to be informed about available rentals than those who didn’t.
When Brown applied for her Memphis apartment five years ago, she said she presented as a man to avoid any potential discrimination.
“It made me feel nervous, it made me feel like I’m doing something wrong, and it made me feel like I was an outcast,” she said. “I had to play the role that they wanted me to play, the role to just give me a place to stay.”
Recent studies indicate that the lack of access to secure housing and employment often puts Black trans people at a dangerous crossroads where they are vulnerable to violence. Between January 2013 and July 2020, Human Rights Campaign, an LGBTQ advocacy group, has tracked at least 180 cases of trans and gender-nonconforming people being violently killed in the U.S., with trans Black women accounting for approximately 70 percent of the deaths.
The violence Black trans women endure is directly related to housing insecurity, Gore said, adding that the COVID-19 pandemic will likely exacerbate the situation.
“That's because we're trying to maintain our housing, so we're doing things that may be a little risky in order to survive and make sure that we do have housing,” she said.
Hill knows this violence firsthand. “I’ve been stabbed in my chest. ... I have been shot. I have been through a lot,” she said.
At the end of June, Hill became homeless again after her landlord raised her rent. But through My Sistah’s House’s tiny-homes campaign, Hill hopes to soon have a house to call her own.
“I still have an opportunity to do what it is that I want to do,” said Hill, who hopes to build a career as a musician. “Stability right now would be overwhelming for me. I'm crying now, because it feels so good and sounds so good.”
Last year, the House of Representatives passed the Equality Act, a federal bill that would broadly modify existing civil rights legislation to ban discrimination against LGBTQ people in employment, housing, public accommodations, jury service, education, federal programs and credit, but the law has been held up in the Republican-controlled Senate.
In the absence of federal protections that would make it illegal for both private and federally funded housing providers to discriminate on the basis of gender identity, including homeless shelters, there is no universal safety net that protects Black trans people from the cycle of poverty, advocates say.
“We'll never be able to eliminate discrimination; it will happen,” Waguespack said. “What we do need is recourse for people who experience it; we need access to justice for those folks, and we need federal, state and local dollars to be moving to folks who are actively working to make housing solutions available to communities that experience this kind of discrimination.”
‘We might have our own town’
My Sistah’s House is currently in negotiations to purchase a plot of land in the Memphis area, where the 20 tiny homes will be installed, according to Gore. The next step, she said, is to purchase the homes (at about $10,000 each) and work with a contractor to ensure they meet building codes. The group also plans to raise additional funds to complete the homes’ interiors and furnish them.
“If it’s successful, we might have our own town in a minute,” said Gore, who hopes to have the project complete by the end of 2020.
In the meantime, Brown imagines how her future tiny house will be adorned: pink and white siding with a black butterfly painted on the side, a rose bush and a swing where she can sit on her front porch with friends.
“Having my own key, just turning my own door into my own home,” Brown said of what she looks forward to the most, “and sitting outside on the porch enjoying the fresh air and the butterflies and just smelling fresh air and freshness and freedom that I can own my own home.”



