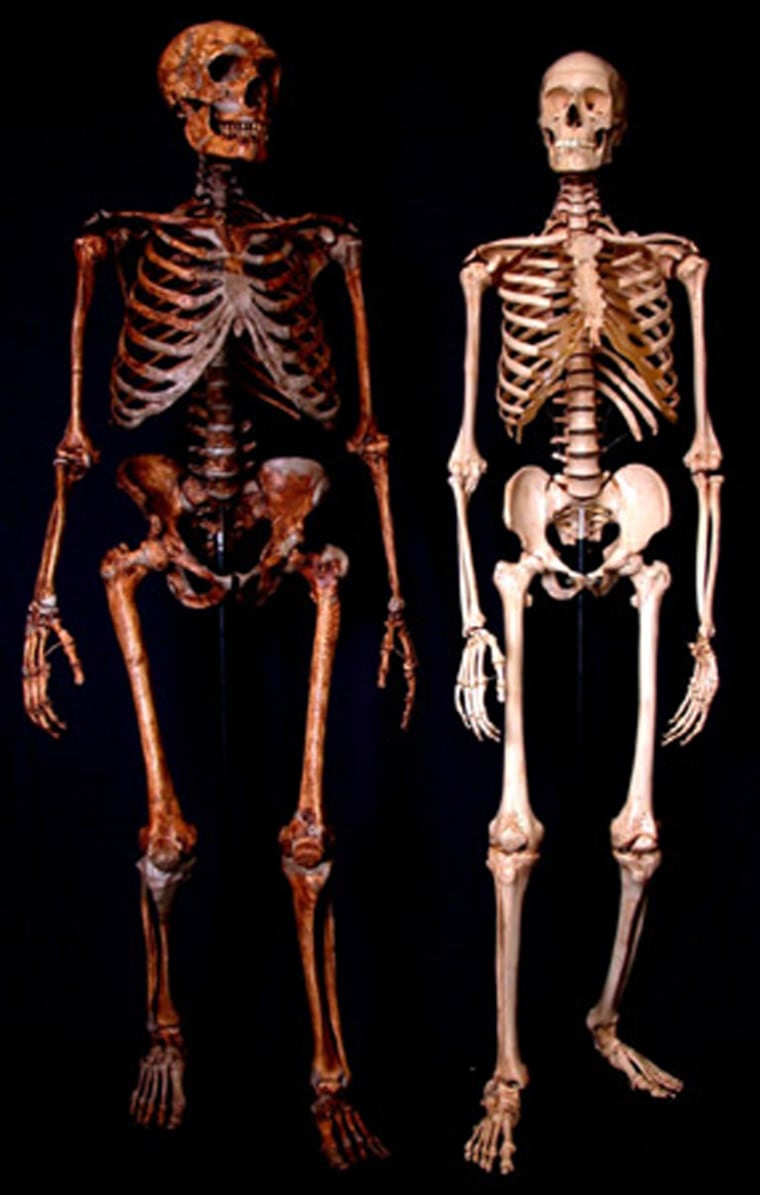
Anthropologists have built a "Frankenstein" Neanderthal skeleton, the first and only full-body reconstruction of the species. The result, announced Thursday, is a shape no one expected.
"It’s almost like making my own fossil discovery," said Gary Sawyer, one of the skeleton’s architects.
Sawyer, an anthropologist at the American Natural History Museum in New York, and his colleague Blaine Maley of Washington University pieced together the skeleton using bones mostly from an individual known as La Ferrassie 1. La Ferrassie 1 was missing its rib cage, pelvis and a few other parts, so Sawyer and Maley had to scrounge around to fill in the gaps.
"The missing parts had to come from another classic Neanderthal that was similar, if not identical, in size to the La Ferrassie man," Sawyer told LiveScience in a phone interview.
The spare parts came from Kebara 2, a 60,000-year-old skeleton discovered in Israel in 1983. Kebara 2 was previously known as the specimen with the best rib cage, pelvis and vertebral preservation.
The La Ferrassie man was discovered in France in 1909 and is about 70,000 years old.
'Dwarfy-like beings'
Sawyer said the replacement bones are remarkably similar in size to La Ferrassie man — most were off by only a few millimeters.
Still, as the scientists pieced together the bones, something didn’t look quite right. A rotund, bell-shaped torso, produced by a flared lower ribcage, and a pelvic region that looked slightly wide and feminine, began to form in front of their eyes.
"The biggest surprise by all means is that they have a rib cage radically different than a modern human’s rib cage," said Sawyer. "As we stood back, we noticed one interesting thing was that these are kind of a short, squat people. These guys had no waist at all — they were compact, dwarfy-like beings."
Other bits and replacement pieces, mostly the ends of bones, were collected from half a dozen other Neanderthals. The remaining gaps were filled in with reconstructed human bones.
The finished product is "like Frankenstein," Sawyer said.
Distant cousins of modern humans
Even though the reconstructed fossil is made up of both Neanderthal and human bones, Sawyer doesn’t believe that modern humans could have evolved from Neanderthals, based on the pelvic and torso discrepancies between the two species.
"There is no way that modern humans, I believe, could have evolved from a species like Neanderthal," Sawyer said. "They’re certainly a cousin — they’re human — but they’re one of those strange little offshoots."
The reconstructed Neanderthal skeleton is currently on display at the Dolan DNA Learning Center in Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.. It will eventually go on permanent display at the American Museum of Natural History.
This research will be published in Friday's issue of the Anatomical Record Part B: The New Anatomist.
Neanderthals were a relative of Homo sapiens that co-inhabited Europe and parts of western Asia with anatomically modern humans from about 120,000 to 29,000 years ago. They were well adapted to the cold and were very muscular — good traits for hunting large animals.
"They had very strong hands," Sawyer said. "If you shook hands with one, he would turn your hand to pulp."