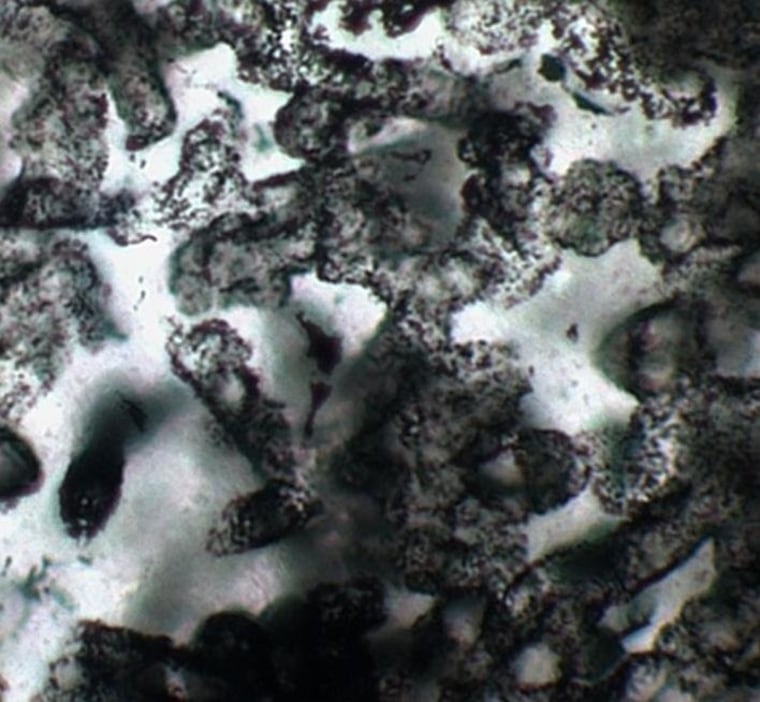
Scientists have found Earth's oldest fossils in Australia and say their microscopic discovery is convincing evidence that cells and bacteria were able to thrive in an oxygen-free world more than 3.4 billion years ago.
The finding suggests early life was sulphur-based — living off and metabolizing sulphur rather than oxygen for energy — and supports the idea that similar life forms could exist on other planets where oxygen levels are low or non-existent.

"Could these sorts of things exist on Mars? It's just about conceivable. This evidence is certainly encouraging and lack of oxygen on Mars is not a problem," said Martin Brasier of Oxford University, who worked on the team that made the discovery.
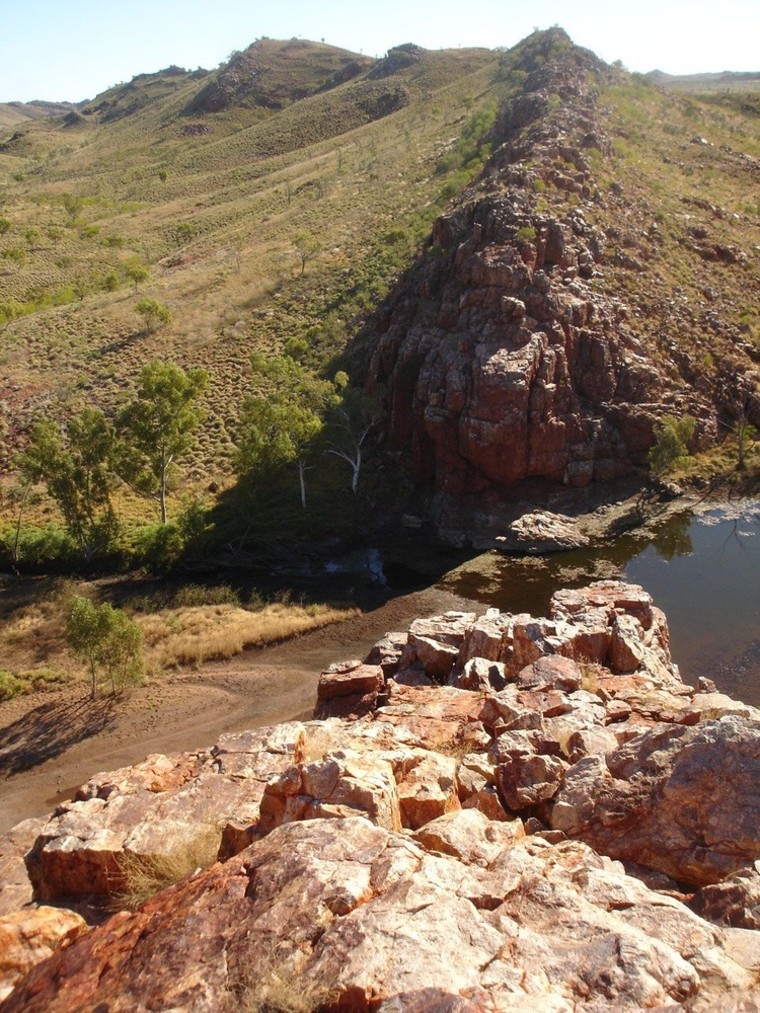
The microfossils, which the researchers say are very clearly preserved and show precise cell-like structures, were found in a remote part of western Australia called Strelley Pool.
In a study published in the journal Nature Geoscience on Sunday, Brasier's team explained that the tiny fossils were preserved between the quartz sand grains of the oldest shoreline known on Earth in some of the oldest sedimentary rocks ever discovered.
"We can be very sure about the age as the rocks were formed between two volcanic successions that narrow the possible age down to a few tens of millions of years," he said. "That's very accurate indeed when the rocks are 3.4 billion years old."
By analyzing the fossils, the rocks they were found in and the surrounding environment, the scientists have built a picture of Earth at this time as a hot, murky, violent place where there was a high and constant threat of volcanic eruptions and meteor strikes.

The sky would have been cloudy and grey, keeping the heat in even though the sun would have been weaker than today, and the oceans would have been around 40-50 degrees Celsius — the temperature of a hot bath.
Most significantly, there was very little oxygen around since there were no plants or algae to photosynthesize and produce it, Brasier explained in a telephone interview.
"It's a rather hellish picture," he said. "Not a great place for the likes of us. But for bacteria, all of this was wonderful. In fact, if you were to invent a place where you wanted life to emerge, the early Earth is exactly right."
The researchers are now using the techniques and approaches they used in this study to re-examine other fossil finds that scientists have suggested may also contain evidence for very early life on Earth.