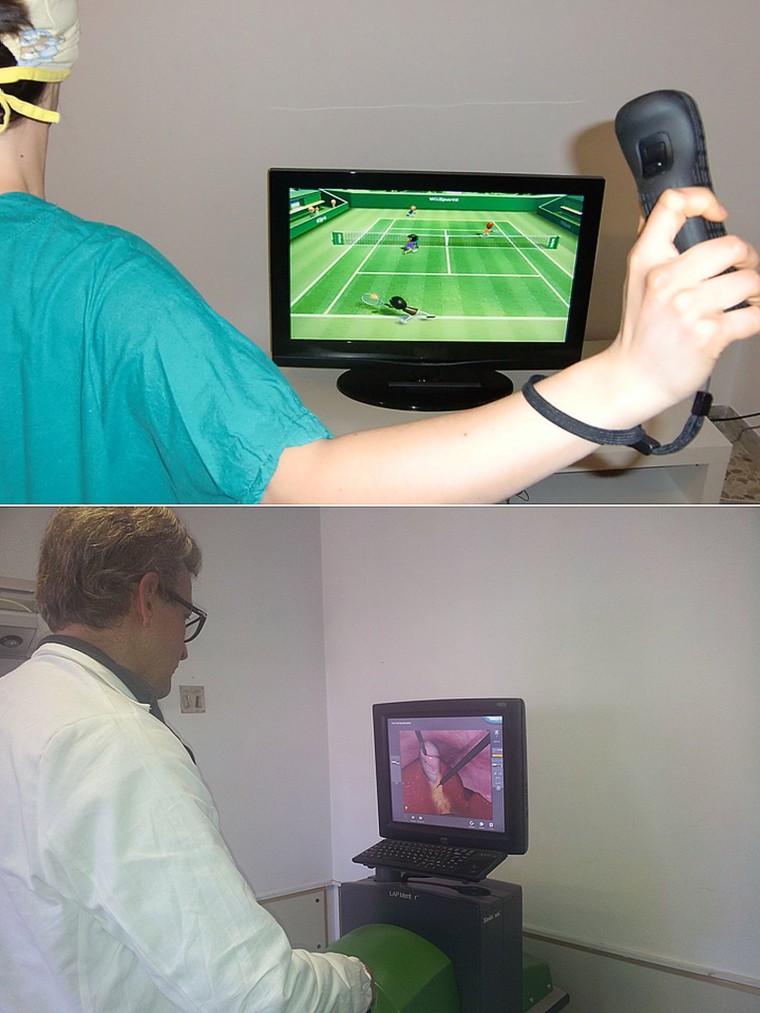
Next time you're about to get a surgical procedure, you might want to ask your doctor whether he or she plays video games.
And it seems the answer you want to hear is: "Yes!"
According to new research conducted at the Sapienza University of Rome in Italy and published Wednesday in the journal PLOS ONE, regularly playing games on a Nintendo Wii can help laparoscopic surgeons improve their performance.
For this study, the researchers looked at whether a four-week, game-playing training regimen on a Wii console would impact the laparoscopic skills of post-graduate surgical residents.
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgery in which a very small camera is inserted into the body along with surgical instruments. The camera allows doctors to see what they are doing on a TV screen while they control the movements of the surgical instruments with a handle outside the body.
The study took 42 subjects (all with low video game experience and low laparoscopic surgery experience) and then assigned half of them a Wii training routine that involved playing three mini games from the "Wii Sports" and "Wii Sports Resort" video games for 60 minutes a day, five days a week, for four weeks. The other half of the group was instructed not to play any video games.
Both before and after the Wii training, all of the participants' skills were tested on a laparoscopic simulator. And while all 42 subjects showed improved skills with the simulator from the first session to the second session, the Wii-trained group showed a significant improvement over the other group in several areas, including economy of instrument movements and efficient cautery, according to the research report.
Dr. Gregorio Patrizi, who lead the research team, told NBC News in an email interview that he expected to see improvements but, "the differences in outcomes between the two groups were far beyond our expectations. What surprised us the most was that almost all the results were clearly statistically significant, even in complex procedures like virtual cholecystectomy," which is done to remove the gallbladder.
The research came about after Patrizi, his colleague Dr. Domenico Giannotti and their team noted something...

"The study arose from an intuition: We noticed that some people were more adaptable at their first attempt on the (laparoscopic) simulator," Patrizi said. "We investigated, almost kidding, to see if they were 'nerds' used to playing video games, and it turned out that there was a strange coincidence..."
The research team noted that some previous studies had shown that prior experience with video game playing could enhance spatial attention and eye-hand coordination in laparoscopic procedures. (Meanwhile, a recent study at the University of Texas found that hours spent with a game controller in hand provides some of the skills needed to perform some of the most advanced robotic surgeries.)
But Patrizi and his colleagues decided to specifically test whether Wii gaming — and a systematic game training routine — would be helpful because of the machine's unique motion-sensing controls.
"The problem in laparoscopy (real and virtual) is that you have to move in a 3-D space with a 2-D view," he said. "The Nintendo Wii is a video-game console with a wireless controller able to detect movement in three dimensions. Thanks to this controller, the gamers can play using physical gestures while traditional video-games require the player to press a button or to move a joystick. Therefore the improvement is based on the fact that the Nintendo Wii, like others recent consoles, provides 3-D video games and accordingly enhances visual attention, depth perception and movement coordination. On the other hand, the group who did not train on the Wii improved mostly according to the familiarization with the simulator."
Patrizi's study concludes, "The Nintendo Wii might be a helpful, inexpensive and entertaining part of the training of young laparoscopists, in addition to a standard surgical education based on simulators and the operating room."
So do these new findings mean that Patrizi now prescribes Wii game playing to surgeons as a means of improving their laparascopic skills?
Patrizi had this to say, "Why not! What it turns out is that training and 'studying' don't need to be boring!"
Winda Benedetti writes about video games for NBC News. You can follow her tweets about games and other things on Twitter here @WindaBenedetti and you can follow her on Google+. Meanwhile, be sure to check out the IN-GAME FACEBOOK PAGE to discuss the day's gaming news and reviews.